Artificial Intelligence has quietly become part of the digital backbone of modern life. It filters spam, recommends content, optimizes logistics, and helps security teams analyze massive volumes of data in real time. In cybersecurity, AI is often framed as a powerful defender—an intelligent layer that can spot threats faster and more accurately than human analysts alone.
But this same intelligence is now being adopted by attackers.
Cybercriminals are increasingly using AI to automate deception, evade detection, and scale attacks with alarming efficiency. This shift represents more than just a technical evolution—it changes how cyber threats behave, spread, and succeed. Welcome to the era of AI-powered cyberattacks, where attacks are no longer static scripts, but adaptive systems capable of learning from their targets.
This article explores how AI-driven cyberattacks work, why they are becoming more common, and what this means for individuals, businesses, and security teams. Rather than focusing on hype, the goal is to provide clarity and practical understanding.
What Are AI-Powered Cyberattacks?

AI-powered cyberattacks are malicious activities that leverage artificial intelligence techniques such as machine learning (ML), deep learning, and natural language processing (NLP) to enhance or automate cybercrime.
Unlike traditional attacks that rely on fixed rules and predictable behavior, AI-driven attacks are adaptive. They observe responses from systems and users, then adjust their tactics accordingly. In practice, this allows attackers to:
- Analyze target behavior and refine attack strategies
- Generate convincing human-like text, audio, or video
- Optimize delivery timing to avoid detection
- Scale personalized attacks without proportional human effort
Rather than simply executing commands, these systems learn what works and improve over time. This adaptability makes them particularly effective against legacy security controls that depend on known signatures or static rules.
How AI Changes the Attacker’s Playbook
From Scripts to Learning Systems
Traditional cyberattacks often rely on scripts—predefined payloads targeting known vulnerabilities. Once detected, these attacks can usually be blocked with signatures or patches.
AI-powered attacks replace this rigidity with learning. The system tests small variations, observes which ones succeed, and gradually refines its behavior. Over time, the attack becomes harder to detect because it no longer looks the same twice.
Personalization at Scale
AI allows attackers to personalize attacks in ways that were previously impractical. A phishing email sent to a finance employee may reference invoices or payment approvals, while one sent to an engineer may mention repositories or system access.
This contextual relevance lowers suspicion. The message feels expected rather than random.
Adaptive Evasion Techniques
Some AI-enabled malware evaluates its environment before acting. If it detects sandboxing, debugging tools, or endpoint protection, it may delay execution or shut down entirely.
This behavior-based evasion is frequently discussed in threat research published by major security vendors.
External reference: Microsoft Security Blog
Real-World Examples of AI in Cybercrime

Deepfake Impersonation Attacks
One of the most visible applications of AI in cybercrime is the use of synthetic audio and video. Attackers generate deepfake voices or videos to impersonate executives, managers, or trusted partners.
These attacks often target employees with authority over payments or access. A familiar voice combined with urgency can override established verification processes.
Authoritative overview: CISA – Deepfakes and Synthetic Media
AI-Generated Phishing Campaigns
Phishing has evolved from generic spam into targeted social engineering. AI-generated emails are grammatically accurate, context-aware, and increasingly indistinguishable from legitimate communication.
This evolution closely aligns with social engineering patterns documented by OWASP.
Reference: Social Engineering (Wikipedia)
Adaptive Malware Behavior
Some modern malware uses machine learning to determine when to execute malicious actions. Instead of acting immediately, it may wait for normal user activity or specific system states, blending into legitimate behavior.
This extended dwell time increases potential impact and complicates forensic investigation.
Why AI-Powered Cyberattacks Are Increasing
The rise of AI-powered cyberattacks is driven by a combination of technical and economic factors:
- Lower barriers to entry: Open-source models and cloud-based AI services are widely accessible.
- Abundant data: Public breaches, social platforms, and leaked datasets provide training material.
- Asymmetric advantage: Attackers only need one success, while defenders must prevent all failures.
In many cases, attackers do not need advanced or proprietary AI. Even moderately capable models can significantly enhance traditional attack techniques.
The Double-Edged Sword: AI in Cyber Defense
While AI enables more sophisticated attacks, it is also a critical component of modern defense strategies.
Behavior-Based Threat Detection
AI-driven security tools analyze behavior rather than relying solely on known signatures. This allows detection of previously unseen threats, including zero-day exploits.
Framework reference: NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Automated Response and Correlation
Security orchestration platforms can automatically isolate systems, revoke credentials, or block traffic when suspicious behavior is detected. AI also excels at correlating signals across logs, endpoints, and networks.
Related internal reading: API Security: Hidden Data Connections
How AI-Powered Attacks Bypass Traditional Security Controls

One of the most underestimated aspects of AI-powered cyberattacks is their ability to bypass traditional security controls without triggering obvious alerts. Many defenses were designed for predictable threats—known malware signatures, repeated attack patterns, or clearly malicious behavior.
AI-driven attacks succeed by doing the opposite.
Fragmented Attack Behavior
Instead of executing a full attack in one sequence, AI-powered malware may break its actions into small, seemingly harmless steps. One system performs reconnaissance, another tests permissions, and a third executes the payload days later.
Individually, these actions rarely raise alarms. Collectively, they form a complete compromise.
Adaptive Timing and Opportunity Windows
AI systems can learn when organizations are least responsive—during weekends, holidays, or shift transitions. Attacks launched during these windows often experience delayed detection and slower response.
This timing-based approach mirrors human attackers, but operates continuously and at scale.
Living-Off-the-Land Techniques
Rather than introducing obvious malware, many AI-assisted attacks abuse legitimate tools already present in the environment. System utilities, cloud APIs, and administrative features are used in unexpected ways.
This technique blends malicious activity into normal operations and aligns with trends documented in the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
Reference: MITRE ATT&CK Framework
The Human Factor: Why People Remain the Primary Target

Despite advances in AI-driven defenses, humans remain the most frequently exploited vulnerability. AI-powered attacks focus heavily on persuasion, trust, and decision-making rather than purely technical exploits.
Trust Exploitation Over System Exploitation
In many real-world scenarios, attackers do not break into systems directly. Instead, they convince someone with access to open the door for them.
AI makes this easier by analyzing communication styles, organizational hierarchies, and response patterns. Messages feel familiar, reasonable, and urgent—often just enough to bypass skepticism.
Automation Bias and Speed Pressure
A common pattern we see is automation bias: people tend to trust messages or requests that appear system-generated or professionally written.
When combined with workplace pressure to respond quickly, this bias creates ideal conditions for AI-powered social engineering.
Related internal reading: How AI-Generated Phishing Sites Trick Users
What We’ve Observed / Practical Notes
In many real-world scenarios, AI-powered cyberattacks are not dramatic or noisy. They are quiet, contextual, and often indistinguishable from normal activity.
A common pattern we see is attackers prioritizing consistency over complexity. They do not need perfect deception—only deception that feels plausible enough in a busy environment.
Another recurring observation is tool overconfidence. Organizations deploy AI-based security solutions but fail to adjust workflows, escalation paths, or verification procedures.
AI cannot replace the role of human decision-making. It amplifies existing strengths—and existing weaknesses.
Common Mistakes That Increase Exposure
- Assuming AI security tools work without tuning or oversight
- Treating phishing awareness as a one-time training task
- Failing to verify urgent or emotional requests
- Overlooking risks to AI systems themselves
- Relying on detection instead of verification
Actionable Steps to Defend Against AI-Powered Threats
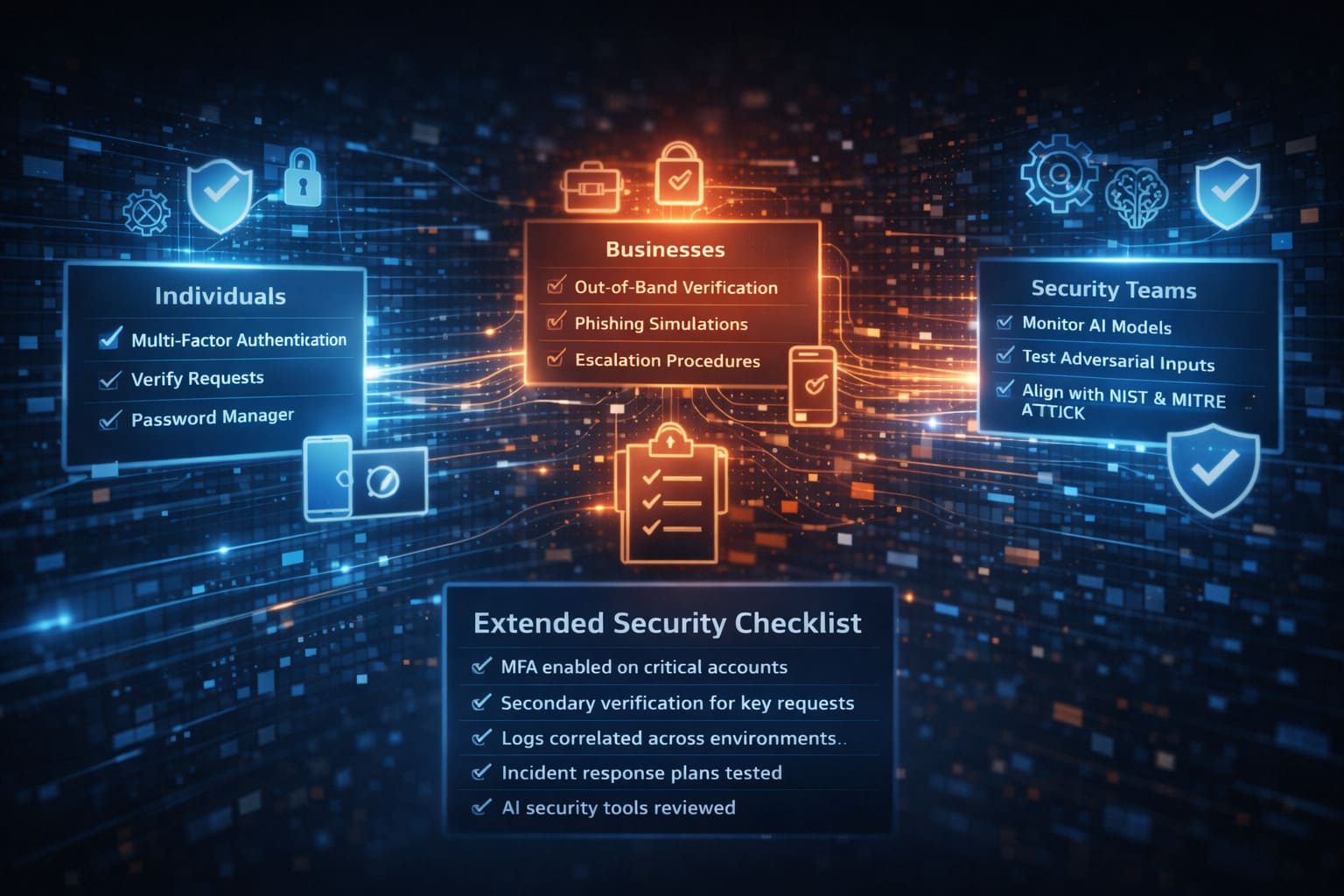
For Individuals
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) on all critical accounts
- Pause and verify unexpected requests, especially involving money or access
- Use password managers to reduce credential reuse
For Businesses
- Require out-of-band verification for financial or access-related requests
- Run regular phishing and impersonation simulations
- Clearly document escalation and verification procedures
For Technical and Security Teams
- Monitor AI models for drift and unexpected behavior
- Test systems against adversarial inputs
- Ensure controls are mapped to recognized frameworks such as NIST and MITRE ATT&CK
Framework references: NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Extended Security Checklist
- MFA enabled on privileged and financial accounts
- Secondary verification required for executive requests
- Logs correlated across endpoints, network, and cloud
- Incident response plans tested through simulations
- AI security tools reviewed for transparency and explainability
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
AI-powered cyberattacks can adapt, learn from responses, and change behavior over time. Unlike traditional attacks that follow fixed patterns, these threats evolve based on what works, making them harder to detect using static security rules.
No. Small and medium-sized organizations are often targeted because they typically have fewer security layers and less formal verification processes. Individuals are also common targets, especially through phishing and impersonation scams.
Yes. AI-generated phishing messages can closely mimic human writing styles, tone, and context. This reduces common red flags such as poor grammar or generic wording, making them much harder to spot.
No. AI security tools are powerful, but they are not a complete solution. They work best when combined with strong processes, user awareness, and clear verification practices.
The most common mistake is acting too quickly without verification. AI-powered attacks often exploit urgency, authority, and familiarity to push people into skipping confirmation steps.
No. Deepfake techniques can also be applied to text, emails, chat messages, and even fake identities across multiple platforms, increasing their effectiveness in social engineering attacks.
Adopting verification habits. Simple actions like confirming requests through a second channel, enabling multi-factor authentication, and questioning urgency can stop many AI-powered attacks before they succeed.
Conclusion: Staying Human in an AI-Driven Threat Landscape
AI-powered cyberattacks rarely announce themselves. They blend into routine, urgency, and familiarity—quietly testing how much we trust what looks normal. The real risk is not advanced technology, but the assumptions we make when speed replaces verification.
As AI continues to shape how attacks are crafted and delivered, security can no longer rely on tools alone. Procedures, policies, and automation matter—but they only work when supported by people who are willing to slow down, question unexpected requests, and verify intent.
Cybersecurity today is less about building perfect systems and more about cultivating mindful habits. In a world shaped by AI, awareness, deliberate pause, and human judgment remain the strongest defenses we have.



