Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming all facets of our daily lives, from communication methods to the ways we secure our digital information. But while AI can strengthen defenses, it also provides powerful tools for hackers to craft smarter, faster, and more evasive cyberattacks. Welcome to the new frontier of cybersecurity, where AI-powered threats are not just possibilities—they’re already here.
What Are AI-Powered Cyber Threats?
AI-powered cyber threats are malicious activities or attacks that use artificial intelligence to enhance their effectiveness. Unlike traditional cyberattacks, which rely on pre-programmed scripts, these threats can learn, adapt, and evolve in real-time.
Key Capabilities of AI in Cyberattacks:
- Automating tasks like vulnerability scanning during cyber attacks.
- Improved phishing campaigns through natural language processing (NLP).
- Adaptive malware that learns how to avoid detection.
- Deepfakes and impersonation for advanced social engineering.
The Rise of AI in the Hacker’s Toolkit
While organizations are investing in AI-driven security solutions, threat actors are doing the same—but for malicious purposes. Machine learning algorithms can now analyze massive amounts of data to identify the best way to exploit systems, craft more believable phishing emails, and bypass traditional firewalls.
Real-World Examples:
- AI-Driven Phishing: In 2023, researchers at IBM demonstrated how AI could generate personalized phishing emails with far greater success than human-written ones.
- Deepfake Impersonation: A UK-based energy firm was scammed out of $243,000 when fraudsters used AI-generated voice deepfakes to mimic a CEO in a phone call.
- Self-Mutating Malware: AI allows malware to reprogram itself in real time, changing signatures to bypass endpoint protection.
For more on the capabilities of deepfake technology, check out Deeptrace Labs.
Types of AI-Powered Cyber Threats
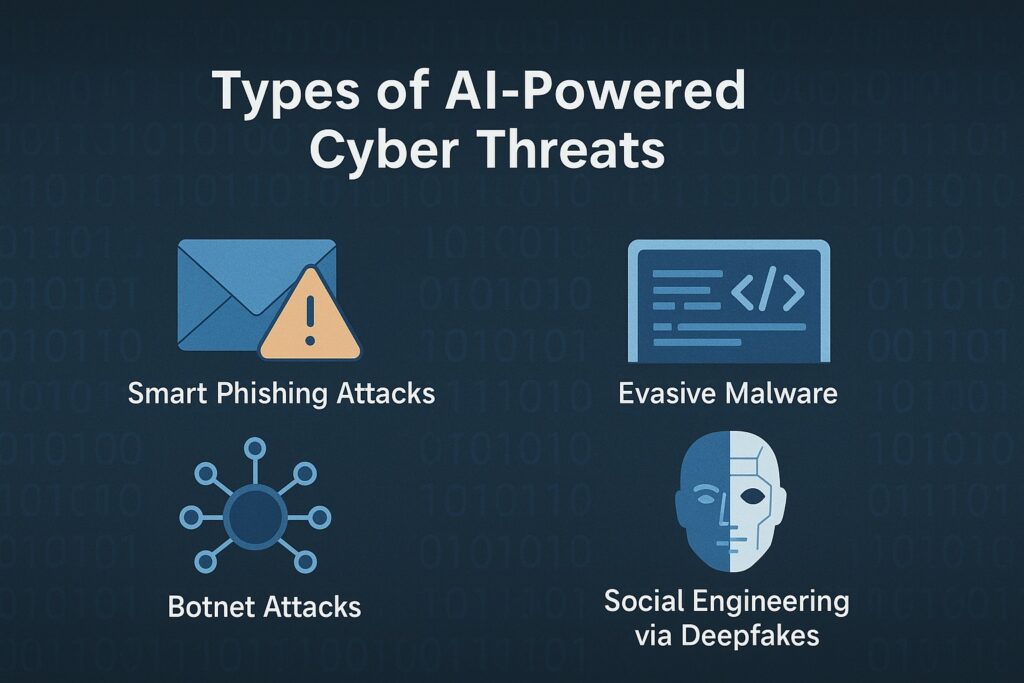
1. Smart Phishing Attacks
Using NLP, AI can craft phishing emails that mimic human tone, grammar, and even cultural context—making them harder to detect and easier to fall for.
2. Evasive Malware
AI is capable of studying how security software operates and adapting malware on the fly to evade detection. These programs are also capable of disabling security tools automatically.
3. Botnet Attacks
Machine learning enhances botnets by enabling coordinated, adaptive attacks on a much larger scale. These bots can learn which servers to hit and when for maximum damage.
4. Social Engineering via Deepfakes
Deepfakes are increasingly used to impersonate voices and faces in real time. These can be deployed in video calls or audio recordings to trick employees into transferring funds or revealing sensitive data.
Why This Matters More Than Ever
As businesses undergo rapid digital transformation and move to cloud infrastructures, their attack surfaces grow exponentially. With AI, cybercriminals can now identify and exploit weaknesses faster than humans can patch them.
According to a 2024 report from Cybersecurity Ventures, global cybercrime costs are expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, a massive leap driven in part by AI-enabled threats.
Challenges in Combating AI Threats
1. Lack of Awareness
Many organizations still rely on outdated security models that are unequipped to handle dynamic AI threats.
2. Skills Shortage
There’s a significant talent gap in cybersecurity. There’s a growing demand for AI experts and cybersecurity analysts skilled in handling AI-driven threats, yet their numbers remain limited.
3. Detection Complexity
Traditional signature-based detection systems can’t keep up with AI-enhanced malware that morphs constantly.
4. Regulatory Grey Areas
AI development outpaces legislation. Currently, there’s little global consensus on the ethical use of AI in cybersecurity.
Defensive Use of AI: Fighting Fire with Fire
Just as attackers use AI to build smarter threats, defenders are using it to build smarter responses.
AI-Based Security Tools:
- User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA): Detects abnormal behavior within networks.
- AI-Powered Endpoint Protection: Monitors endpoint activity and predicts potential breaches.
- Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs): Aggregate data from various sources and use machine learning to detect threats early.
Companies like Darktrace and CrowdStrike are leading the way in providing AI-driven threat detection and incident response.
Best Practices for Organizations
- Invest in next-gen antivirus tools and machine learning-based firewalls.
- Train employees on how to recognize social engineering and phishing attempts.
- Regularly update security policies and tools.
- Stay updated on emerging threats via resources like Krebs on Security and The Hacker News.
- Perform routine audits to maintain compliance and uncover emerging threats.
What Individuals Can Do
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Always check the source before opening links or downloading any attachments.
- Keep all software and devices updated.
- Use strong, unique passwords with a password manager.
The Future of AI and Cybersecurity
Looking ahead, we can expect:
- Smarter AI defense tools that can predict and neutralize threats.
- Increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks that use AI to automate and evolve.
- More government regulations around the use of AI in digital security.
Conclusion: The Arms Race Has Begun
The cybersecurity battlefield is shifting. AI is the newest and most powerful weapon—used by both defenders and attackers. Organizations and individuals alike must understand the risks and adopt proactive, AI-driven defenses.
AI-powered threats aren’t a problem of the future—they are today’s reality. The question is not if you’ll encounter them, but when. Are you prepared?



